How to operate a drone is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything you need to know to safely and effectively pilot your drone, whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills.
We will explore the essential components of a drone, detailing their functions and importance in ensuring safe and efficient flight. We’ll then guide you through the critical pre-flight procedures, emphasizing the significance of calibration and safety checks. The guide will progress to cover takeoff and landing techniques, flight controls, GPS navigation, camera operation, safety regulations, troubleshooting, and even advanced features like obstacle avoidance.
By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge and confidence to confidently take to the skies.
Drone Components and Terminology: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the individual components of a drone and the terminology used to describe them is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will break down the key parts of a drone and define common terms you’ll encounter.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the integrated work of several key components. Let’s explore each one.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. The speed and coordination of these motors are controlled by the flight controller.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this component receives input from various sensors and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It processes data from the GPS, IMU, and other sensors.
- Battery: The power source for the drone, typically a Lithium Polymer (LiPo) battery, providing the energy for the motors and other electronics. Battery capacity determines flight time.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): This system allows the drone to determine its location and maintain position, crucial for features like automated flight and Return-to-Home (RTH).
- Camera: The imaging system, capturing photos and videos. Features vary greatly between drones, including resolution, sensor size, and image stabilization capabilities.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms is essential for understanding manuals, online resources, and discussions within the drone community.
- Altitude Hold: The drone maintains a constant height above the ground.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing camera shake and improving image quality.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): A sensor that measures the drone’s orientation and movement.
- RTH (Return to Home): A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point.
- Payload: The weight of the camera and any other equipment attached to the drone.
- Firmware: The software that controls the drone’s hardware.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different types of batteries offer varying performance characteristics. Understanding these differences is vital for selecting the right battery for your needs and ensuring safe operation.
| Type | Voltage | Capacity (mAh) | Flight Time (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S | 11.1V | 1300-5000 | 15-30 minutes |
| LiPo 4S | 14.8V | 1500-6000 | 20-40 minutes |
| LiHV (High Voltage LiPo) | 12.6V (3S) / 16.8V (4S) | 1300-5000 | Slightly longer than equivalent LiPo |
| LiFePO4 | 3.2V per cell | Variable | Comparable to LiPo, often with longer lifespan |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This step-by-step checklist should be followed before every flight to mitigate risks.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage to propellers, motors, or body.
- Check battery level and ensure it is properly connected.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (instructions vary by drone model).
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring proper connection.
- Check the camera settings and ensure it’s functioning correctly.
- Select the appropriate flight mode.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration check as prompted by the drone’s software.
- Review local regulations and ensure you’re flying in a permitted area.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Accurate compass and sensor calibration are critical for stable flight and accurate positioning. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior and potential crashes. The specific calibration procedure varies between drone models, so consult your drone’s manual for detailed instructions. Generally, this involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern or following on-screen prompts within the drone’s application.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual flowchart helps streamline the pre-flight process and ensures no steps are missed. (Imagine a flowchart here showing the steps from the checklist above, with boxes representing each step and arrows indicating the sequence. Start with “Inspect Drone,” proceed through each step, and end with “Ready for Takeoff”).
Taking Off and Landing
Proper takeoff and landing techniques are paramount for safe drone operation. These procedures minimize the risk of accidents and damage to the drone.
Safe Takeoff Techniques
A smooth and controlled takeoff is essential. Start by placing the drone on a level surface, free from obstacles. Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a strong GPS signal. Most drones offer assisted takeoff features that simplify the process, gradually increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Always monitor the drone’s altitude and position during takeoff.
Smooth Landing Procedures
A controlled descent and landing are crucial to prevent damage. Begin by gradually decreasing the throttle, allowing the drone to descend smoothly. Aim for a gentle landing on a level surface. Avoid sudden movements or abrupt changes in throttle, which can lead to a hard landing or crash. Many drones offer assisted landing features, providing a more controlled descent.
Takeoff and Landing Methods Comparison
Different takeoff and landing methods cater to varying skill levels and environmental conditions.
- Assisted Takeoff/Landing: These features simplify the process, especially for beginners, by automating throttle control during ascent and descent.
- Manual Takeoff/Landing: This requires more skill and precise control of the throttle, offering greater control but increasing the risk of errors for less experienced pilots.
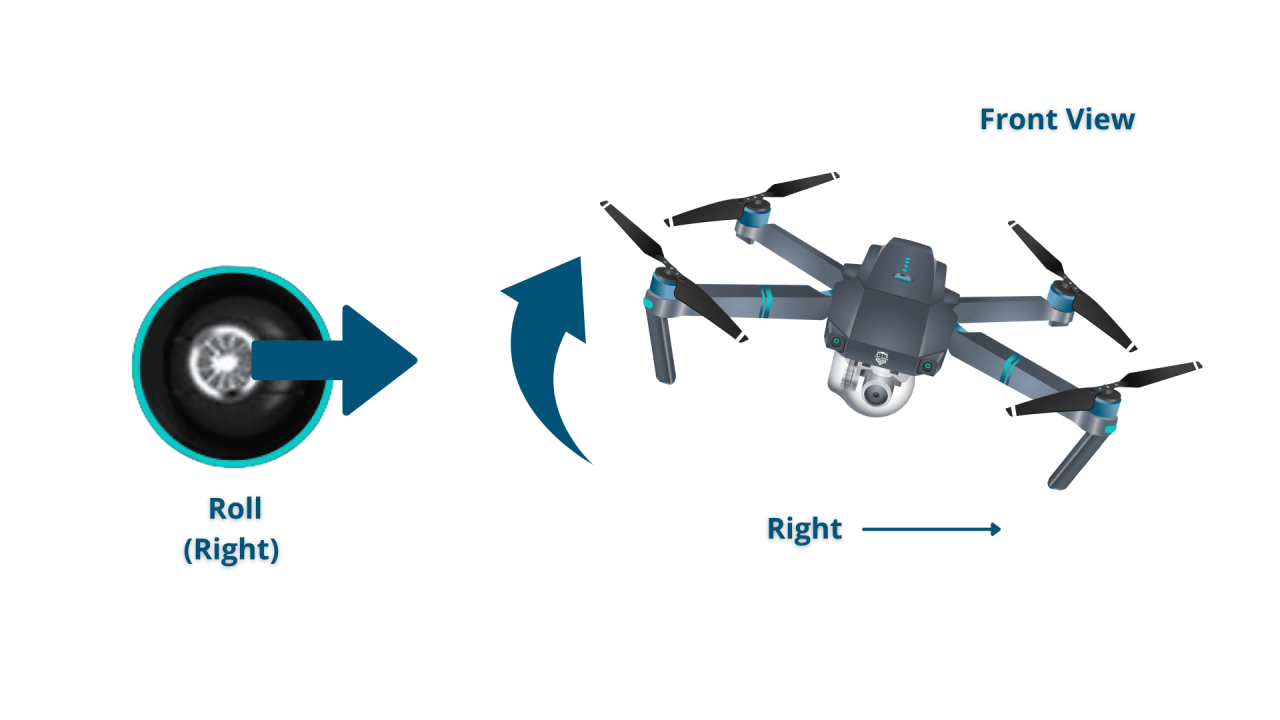
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding drone flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section will explain the functions of the control sticks and how to perform basic maneuvers.
Flight Control Stick Functions
Most drones use two control sticks: one for controlling altitude and movement along the drone’s longitudinal axis (forward/backward and up/down), and the other for controlling the drone’s lateral axis (left/right and rotation).
- Left Stick (Throttle/Pitch): Vertical movement (up/down) is controlled by the stick’s vertical movement. Forward/backward movement is controlled by the stick’s forward/backward movement.
- Right Stick (Roll/Yaw): Lateral movement (left/right) is controlled by the stick’s left/right movement. Rotation (yaw) is controlled by the stick’s rotational movement.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering these basic maneuvers is crucial before attempting more advanced flight techniques.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing the drone’s altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing the drone’s altitude.
- Turning: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis.
Progressive Flight Maneuvers
Practice these maneuvers in a safe and open area, gradually increasing the complexity as your skills improve.
- Hovering practice: Maintain a stable hover for extended periods.
- Controlled ascents and descents: Practice smooth transitions between altitudes.
- Precise turns: Execute smooth, controlled turns at various speeds.
- Figure-eight maneuvers: Combine turns and altitude changes.
- Forward and backward flight: Practice controlled movement in these directions.
- Sideways flight: Practice controlled movement in these directions.
Navigating with GPS and Waypoints
GPS plays a vital role in drone navigation and stability, enabling features like automated flights and precise positioning. This section explains how to utilize GPS and waypoints for efficient drone control.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the fundamentals is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. This website covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring a safe and successful flight experience for all levels of drone pilots.
GPS Assistance in Drone Navigation and Stability
GPS provides the drone with its location, allowing it to maintain its position and altitude. This is especially crucial in windy conditions or when performing complex maneuvers. The drone uses this data in conjunction with its IMU to maintain stability and execute commands accurately.
Setting and Using Waypoints
Waypoints allow you to program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. Most drone software allows you to set waypoints on a map, defining the drone’s route. The drone will then automatically navigate between these points, maintaining the specified altitude and speed.
GPS Limitations
GPS accuracy can be affected by various environmental factors.
- Urban Canyons: Tall buildings can obstruct GPS signals, leading to reduced accuracy and potential signal loss.
- Mountainous Areas: Similarly, mountains can block GPS signals, affecting navigation.
- Signal Interference: Electronic interference can also affect GPS accuracy.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera settings and techniques is essential for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section will guide you through optimizing your camera settings and achieving professional-looking results.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Adjusting camera settings allows you to control various aspects of image quality.
Learning to operate a drone safely and effectively involves understanding its controls and limitations. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the regulations governing drone operation in your area. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering the basics will allow you to confidently and responsibly enjoy the exciting world of drone piloting.
- Resolution: Higher resolution means more detail but larger file sizes.
- Frame Rate: Higher frame rates result in smoother videos but require more storage space.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise.
Optimal Image Stabilization

Achieving sharp, stable footage is crucial for professional-looking results. Using a gimbal significantly reduces camera shake. Flying smoothly and avoiding sudden movements also helps minimize image blur. Many drones also incorporate electronic image stabilization (EIS) to further enhance stability.
Adjusting Camera Angles and Framing

Experiment with different camera angles and framing to create compelling shots. Consider using various perspectives to add visual interest to your footage.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation requires adherence to safety regulations and best practices. This section will Artikel key guidelines to ensure safe and legal drone flying.
Drone Safety Regulations
Drone regulations vary by country and region. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. Common regulations include registration requirements, flight restrictions in certain airspace (near airports, etc.), and limitations on flight altitude and distance.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible flying involves more than just following the rules. It’s about being aware of your surroundings and minimizing risks.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near people or property.
- Never fly in adverse weather conditions.
- Be mindful of airspace restrictions.
- Respect privacy and avoid filming people without their consent.
Best Practices for Safe and Ethical Drone Flying
Adhering to best practices helps prevent accidents and promotes responsible drone use.
- Regularly inspect your drone for damage.
- Always use a fully charged battery.
- Fly in well-lit areas.
- Avoid flying near power lines or other hazards.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Even with careful operation, drones can experience malfunctions. This section will Artikel common problems and troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Several issues can arise during drone operation.
- Low Battery: The most common issue, often resulting in a sudden loss of power and a crash.
- GPS Signal Loss: Can lead to erratic flight behavior and loss of control.
- Motor Failure: A motor malfunction can cause the drone to become unstable or lose control.
- Propeller Damage: Damaged propellers can affect flight stability and performance.
- Software Glitches: Software errors can cause unexpected behavior.
Troubleshooting Steps
Addressing malfunctions promptly can prevent further damage.
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately and replace or recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception or restart the drone.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor for damage and replace it if necessary.
- Propeller Damage: Replace any damaged propellers.
- Software Glitches: Try restarting the drone and controller. Consider updating the firmware if necessary.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends the life of your drone and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
- Inspect the drone after each flight for any damage.
- Clean the propellers and body regularly.
- Store the drone and batteries properly.
- Keep the firmware updated.
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires skill and understanding of various techniques. This section provides tips for achieving professional-looking results.
Techniques for High-Quality Aerial Media, How to operate a drone
- Plan your shots: Scout your location beforehand and visualize your desired shots.
- Use the Golden Hour: The soft light during sunrise and sunset creates beautiful images.
- Master composition: Use the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing shots.
- Experiment with angles: Try different angles to capture unique perspectives.
- Adjust settings for optimal exposure: Use manual settings to control exposure for the best results.
- Smooth movements: Avoid jerky movements to create stable footage.
- Edit your footage: Post-processing can enhance your images and videos.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with creative expression. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of safe and responsible drone piloting, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the skies with confidence. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to safety regulations are crucial for enhancing your skills and ensuring the longevity of your drone.
Embrace the challenges, celebrate your successes, and most importantly, fly responsibly.
Questions and Answers
What type of license or registration do I need to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements regarding drone registration and licensing.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant changes in magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately initiate a controlled descent and return to your starting point. Many drones have “return-to-home” functionality for such situations.
How do I clean my drone’s propellers?
Gently clean propellers with a soft cloth and mild detergent to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store LiPo batteries in a cool, dry place, away from flammable materials. Store them at around 50% charge to maximize their lifespan.
